Pythons list or array methods extend() and append() appears similar, but they perform different operations on the list. Let’s see the differences between extend() and append() list methods.
Extend() vs Append()
| # | Extend() | Append() |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The extend() list method adds the elements from the given iterable like list or array to the current list. | The append() list method add the given list or array to the current list. |
| 2 | For example, if you extend a list of [1, 2, 3] with another list [4, 5], then the resultant list will have 5 elements i.e. [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. | On the other hand, if you append a list of [1, 2, 3] with another list [4, 5], then the resultant list will have just 4 elements i.e. [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]. |
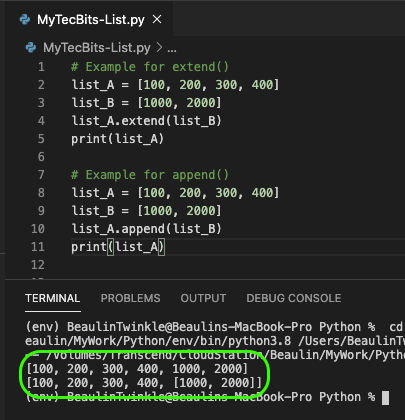
| 3 | Sample code for extend(): list_A = [100, 200, 300, 400] list_B = [1000, 2000] list_A.extend(list_B) print(list_A) Result: [100, 200, 300, 400, 1000, 2000] | Sample code for append(): list_A = [100, 200, 300, 400] list_B = [1000, 2000] list_A.append(list_B) print(list_A) Result: [100, 200, 300, 400, [1000, 2000]] |
# Example for extend()
list_A = [100, 200, 300, 400]
list_B = [1000, 2000]
list_A.extend(list_B)
print(list_A)
# Example for append()
list_A = [100, 200, 300, 400]
list_B = [1000, 2000]
list_A.append(list_B)
print(list_A)
Related Articles
- How to check if a list is empty or not in python?
- How to get the last element of a list in Python programming?
Reference
- More about Python list method at Python Docs.
